Political punch in a package of charm
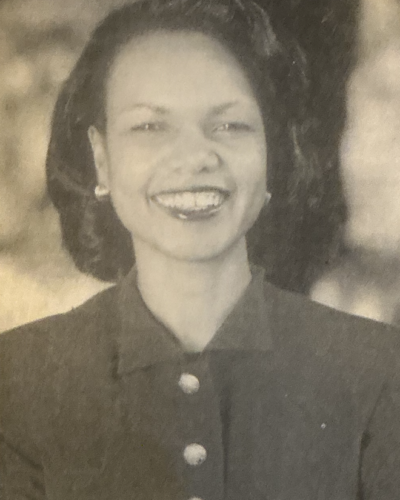
Condoleezza Rice has rarely heard a question she doesn’t know how to answer, from queries about her tumultuous childhood in segregated Alabama to her success in the male world of superpower politics, nuclear weapons and arms control.
She meets me with the friendly smile and easy hospitality of a west-coaster, defying the image of someone anointed by Washington insiders to become the most powerful woman in the world in a year. The chief foreign policy adviser to Republican presidential candidate George W. Bush, Rice is being tipped as a likely secretary of state or national security adviser should Bush win the White House.
As huge a task as this sounds, Rice’s own life story has the word “amazing” written all over it. At 45, she has been the first black woman in just about any job she’s taken on: from special assistant for national security affairs to President George Bush when she was only 34, to provost of California’s prestigious Stanford University (the Harvard of the west coast) where she managed a budget of nearly $2bn…